Workplace accidents and injuries have the highest median loss cost of all roofing-related losses, according to Advisen loss data. Common causes of loss include slips, trips, falls, injuries caused by falling objects, automobile accidents, flammable materials and exposure to malfunctioning electrical equipment.
Some losses can be fatal. In fact, in 2020, roofers had 47 fatal injuries for every 100,000 full-time employees, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Roofers have the third-highest frequency of workplace fatalities—only behind fishers and loggers.
Consider the following roofing injury examples in Advisen’s loss database:
While scoping a roof in 2021, an employee of commercial roofing company Tip Top unwittingly stepped through a skylight. The 20-foot fall resulted in a broken spine and brain injury. In a lawsuit filed shortly after the fall, plaintiffs sued for negligence, alleging the worksite failed to provide warnings, skylight guardrails or covers to alert personnel to the fall hazard.
A similar accident happened in 2016, in which an employee fell from a roof onto concrete during the scope of his job with J & G Roofing Co., Inc, resulting in a traumatic brain injury. The parties reached a $3.7 million settlement.
Frequency of Roofing-related Losses by Type
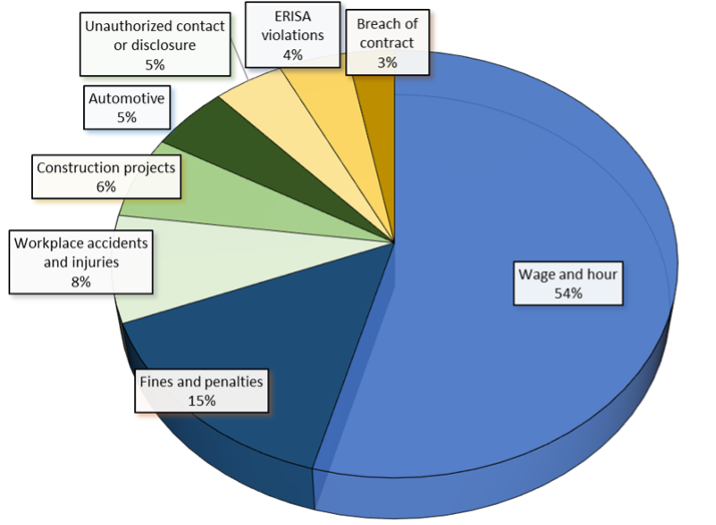
Workplace accidents and injuries were the third-most frequent type of roofing loss—behind wage and hour losses and fines and penalties, according to Advisen data. Fines and penalties are typically issued as the result of unsafe working conditions for roofers and may be incurred following serious workplace injuries.
Examples of fines and penalties in Advisen’s loss database include a $1.8 million OSHA fine against Kehrer Brothers Construction and D7 Roofing in 2015. The fine was issued for allegedly not warning employees about the dangers of removing asbestos and not providing safety methods to limit exposure. Additionally, a $645,000 fine was levied against America 1st Roofing & Builders Inc. for safety violations associated with exposing workers to fall hazards.
Median Cost of Roofing-related Losses
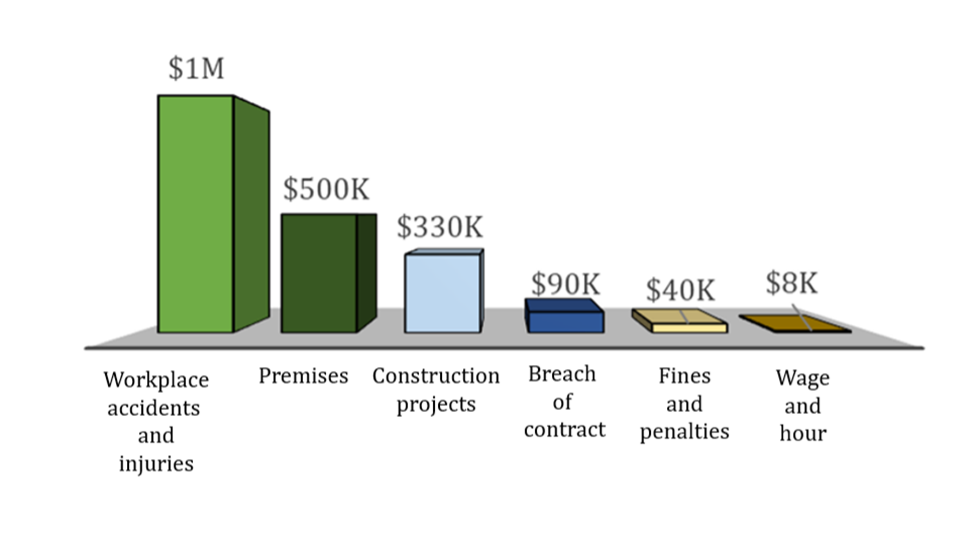
Looking at the severity of the most frequent types of roofing-related losses, workplace accidents and injuries had the highest median loss value at $1 million. Premises losses, which include damages from unsecured construction objects and falling scaffolding, had a median loss cost of $500,000, according to Advisen loss data.
Safety and Risk Management
To prevent safety exposures and potential losses, roofers should follow these risk management tips:
- Employee training—Every employee should know basic safety procedures that will help them recognize and minimize on-the-job risks. Training is not a one-off event. Employees should be refreshed frequently on proper safety protocols.
Fire prevention—There is also a risk of fires on hot work roofs in commercial roofing. To mitigate fire risks, all debris and combustible materials should be removed from roofs and a fire watch should be done after all torching applications. All torching should stop at least three hours from the end of the workday, and the roof should be inspected for hot spots before leaving the worksite.
- Tarping safety—Roof tarping is another area of caution. Tarps can get very slippery when wet and may also conceal tripping or fall hazards such as skylights and vents. Tarps should never be installed when it’s windy or raining. Electrical lines should also be identified before tarping to prevent electrocution.
- Fall prevention—Falling is one of the major injury risks for roofers and may stem from many causes. Inclement weather, for example, can make equipment or shingles slippery, leading to falls. It’s best to postpone work during poor weather conditions. Proper safety equipment such as harnesses, guard rails and fall restraints should be used to prevent fall risks as much as possible. At sites where traditional fall protection equipment isn’t feasible or would cause a greater hazard to employees, a site-specific written protection plan should be implemented to ensure employees are still operating safely.
- Ladder safety—Ladders can also pose a significant hazard, which is why OSHA regulations for ladder safety require regular ladder training for employees and frequent ladder inspections. To prevent injuries to employees or damages to property, ensure ladders are always securely fastened to the roof and placed on a level surface. Damaged ladders should never be used.
- Falling objects—Falling objects also pose a serious threat of injury. To prevent materials from falling, all materials and equipment should be stored at least 6 feet from the roof edge unless a guard rail system is in place. Canopies can also prevent falling objects, but must be strong enough to prevent collapse or penetration of falling objects.
For additional insights and risk management resources, contact us today.
© Zywave, Inc. All rights reserved.
